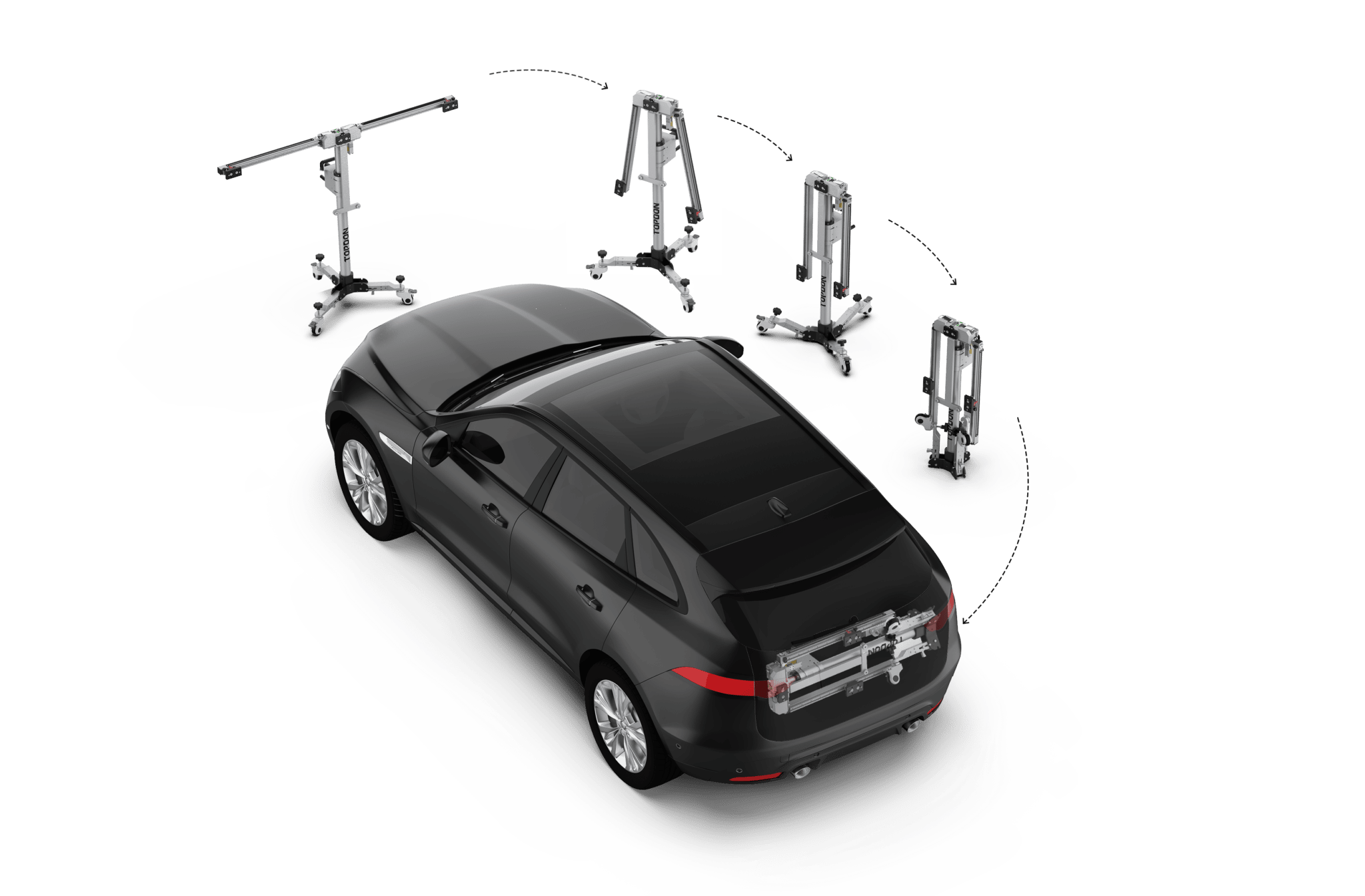
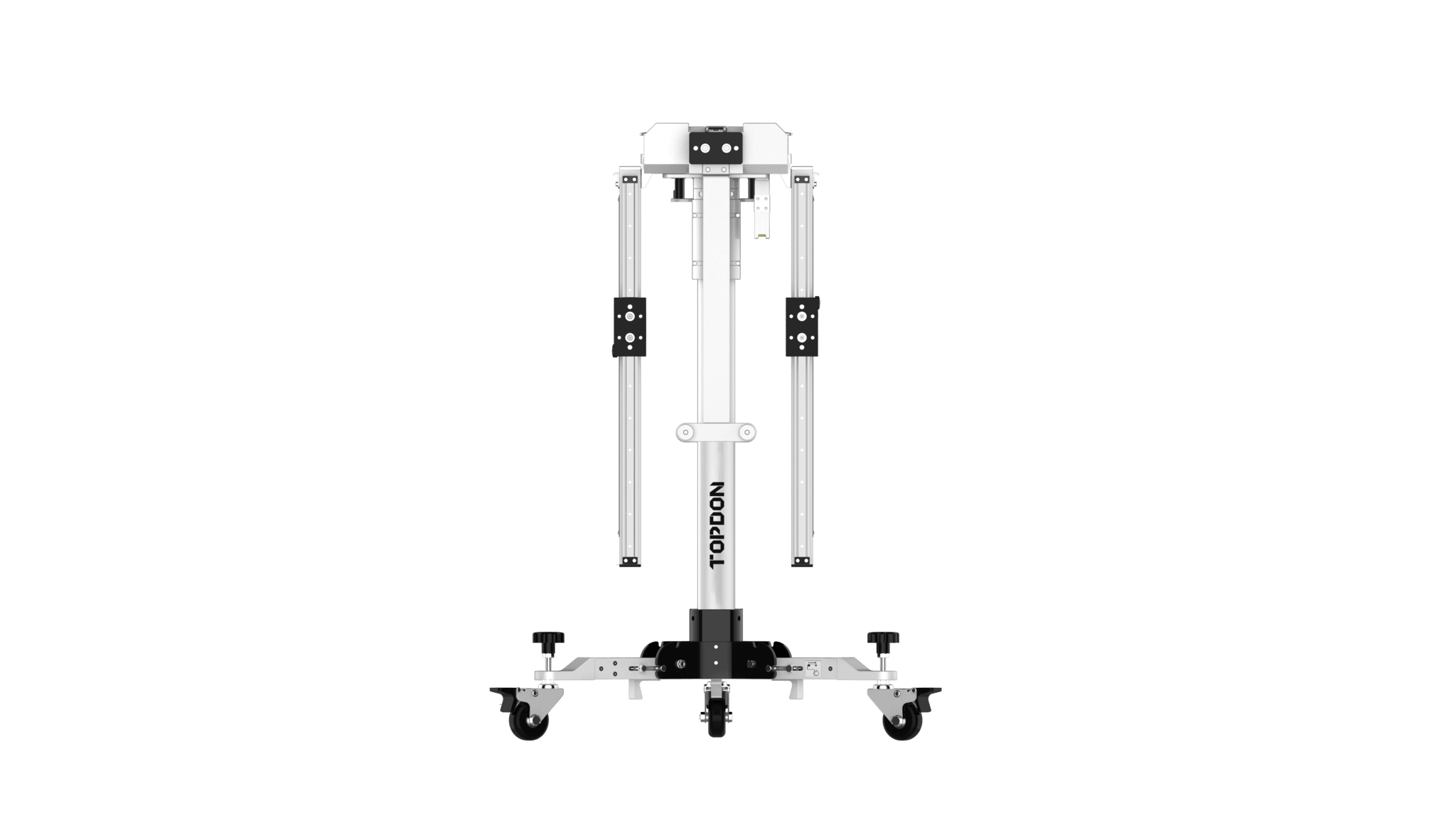
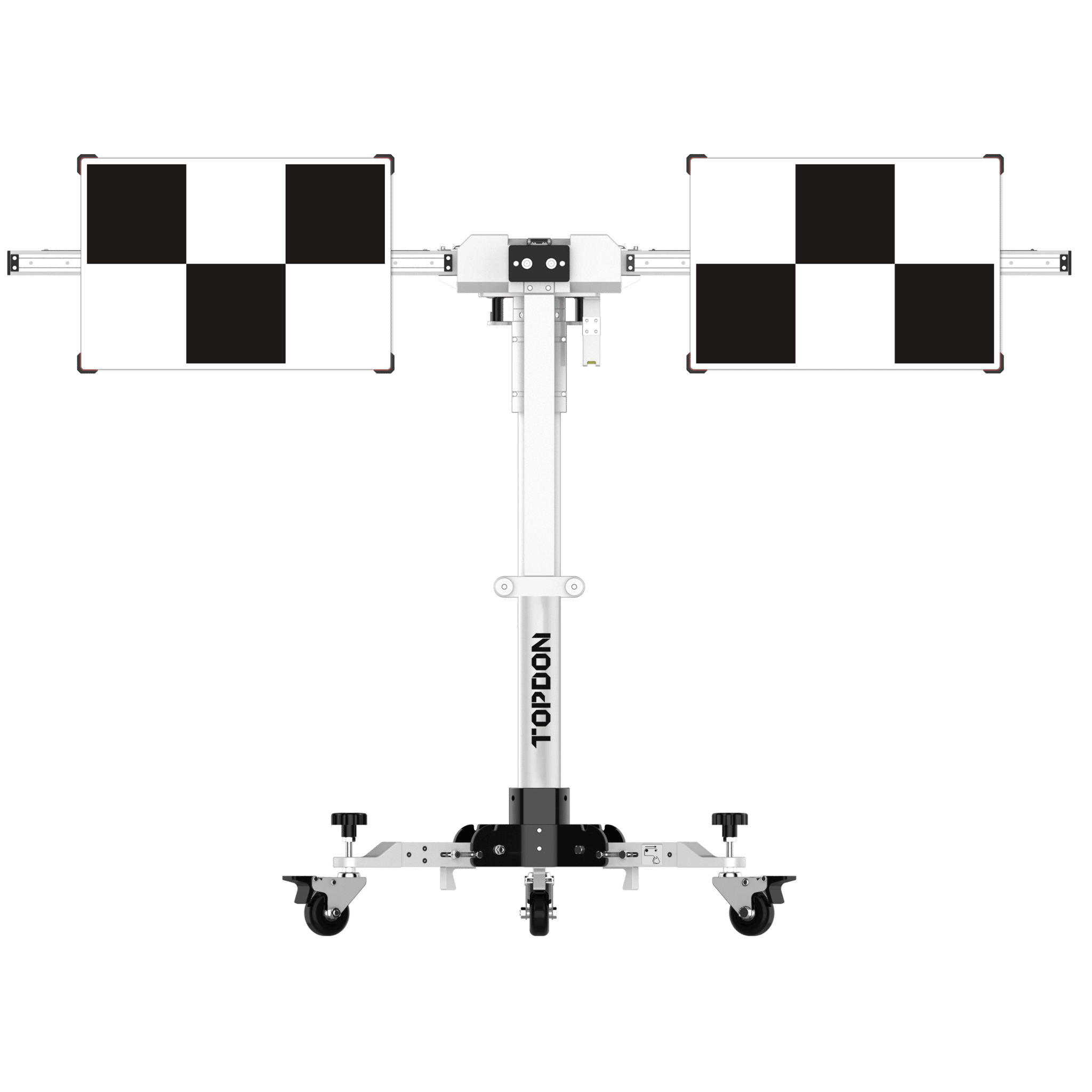
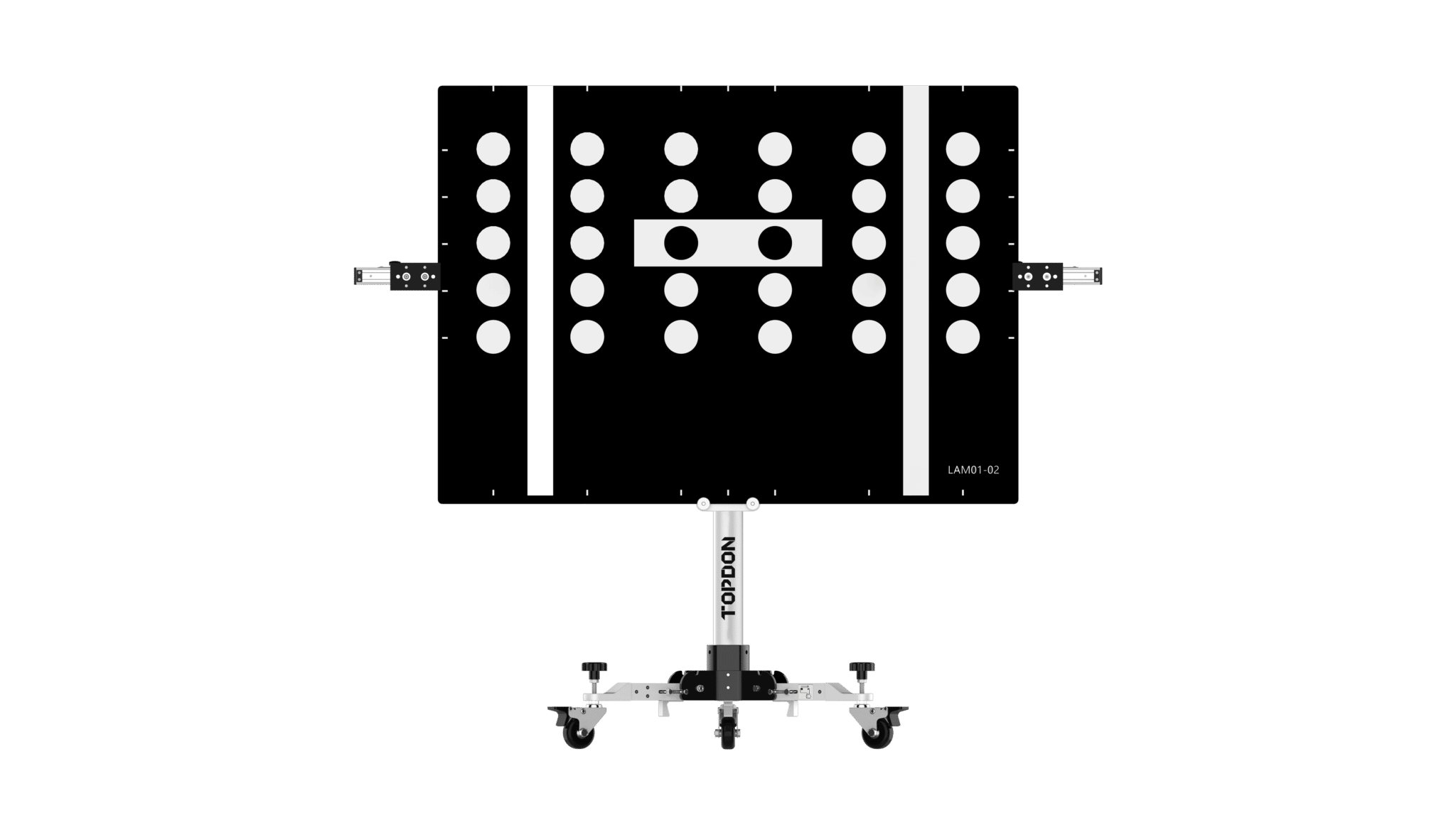
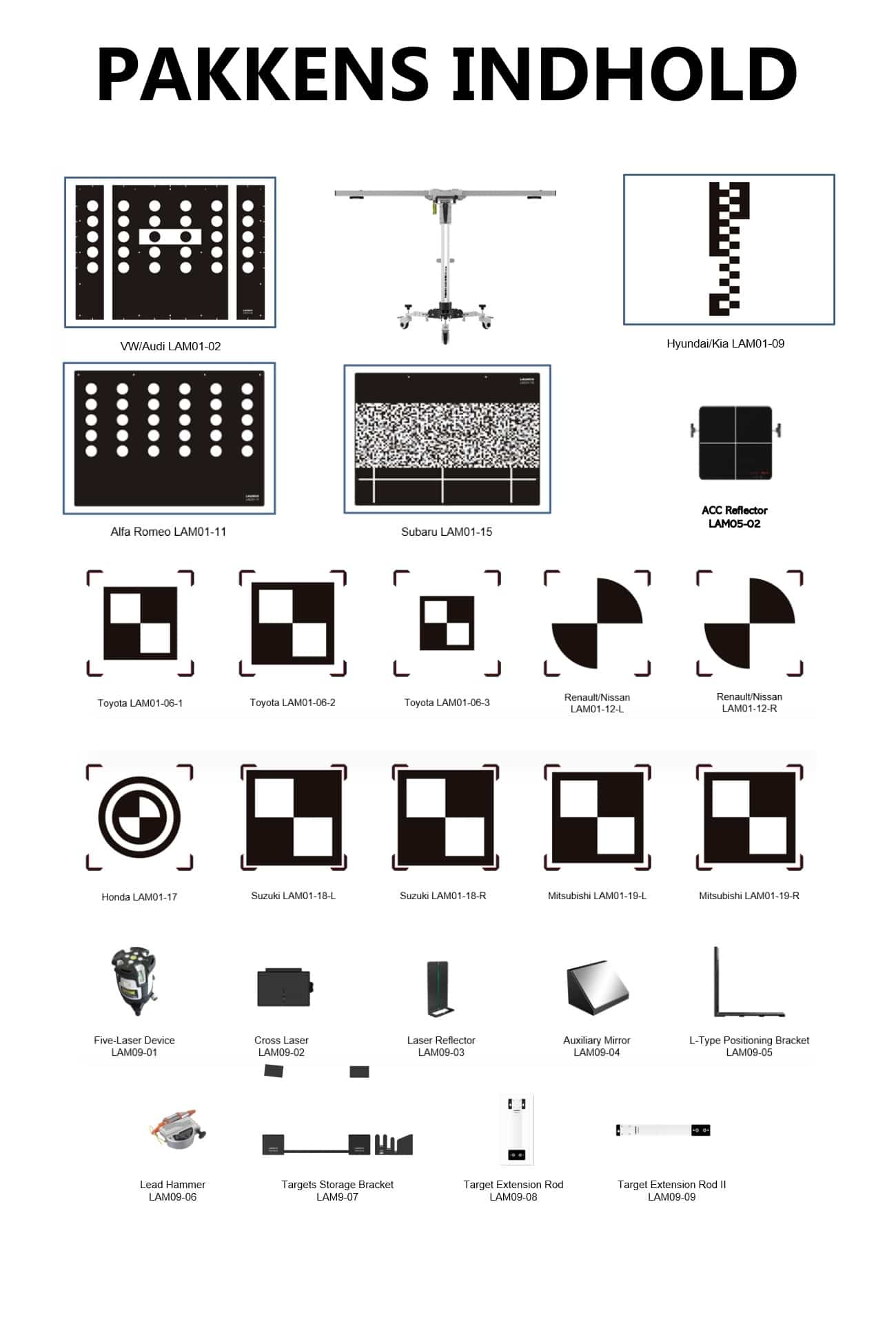
TOPDON – ADAS Mobile
Item number: TADAS
75.000,00 kr.
Incl. VAT
Excl. VAT. VAT
- Easy folding device
- Compatible with Topdon diagnostic tools
- 1. month support 0,-
Specifications
calibration of
Radar
calibration of
LiDAR
calibration of
Night Vision and Ultrasonic sensors
Available on backorder
- 1-3 Day Delivery
- WHAT IS ADAS?
Advanced Driver Assistance System (ADAS) uses image processing cameras, radar, light detection,
range and other sensors to monitor the vehicle’s surroundings and detect potentially dangerous situations.
The purpose is to increase safety through advanced situations and reduce traffic accidents.
Sensors used in ADAS are cameras, Radar, LiDAR, Night Vision and Ultrasonic sensors.
These sensors work with other vehicle systems to monitor condition, movement and stability.
Usually, these sensors are located in the front and rear bumpers, side mirrors, grille and windshield.
- PASSIVE ASSIST SYSTEMS
- A passive system with ADAS monitors the conditions around the vehicle. Warns the driver via lights, message centers,
beeps and / or vibrations of components such as seats, steering wheel, brake pedals or seat belts.
It can also be live graphics / images via screens to help the driver. - LDW – Lane Departure Warning
- RCW – Rear Collision Warning
- AVM – Around View Monitoring
- BSD – Blind Spot Detection
- FCW – Front Collision Warning
- NVS – Night Vision System
- ACTIVE ASSIST SYSTEMS
- An active ADAS system will brake, stop or turn the vehicle from an object.
Situations (such as lane changes) using the electronic power steering module, electronic brake, ABS modules and dampers in PCM.
It can also use sensors to park a vehicle or adjust the headlights to the position of the steering wheel. - AEB – Automatic Emergency Braking
- ACC – Adaptive Cruise Control
- LKA – Lane Keep Assist
- AFL – Adaptive Front Lighting
- AP – Assisted or Automatic Parking
- FCA – Front Collision Avoidance
- To see and read more, check out the attached PDF under the product.
Related products
No related products found.